bind
pronunciation
How to pronounce bind in British English:
UK [baɪnd]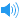
How to pronounce bind in American English:
US [baɪnd]

-
- Noun:
- something that hinders as if with bonds
-
- Verb:
- stick to firmly
- create social or emotional ties
- make fast; tie or secure, with or as if with a rope
- wrap around with something so as to cover or enclose
- secure with or as if with ropes
- bind by an obligation; cause to be indebted
- form a chemical bond with
- provide with a binding
- fasten or secure with a rope, string, or cord
- cause to be constipated
Word Origin
- bind
- bind: [OE] Band, bend, bind, bond, and bundle can all be traced back ultimately to an Indo- European base *bhendh-, which was also the source of Sanskrit bandh ‘bind’ and Greek peisma ‘cable’. In the case of bind, the immediate precursor of Old English bindan was the Germanic stem with an i vowel, *bind-. In the 14th century the verb came to be used as a noun, for the ‘stem of a climbing plant’, from which we get bine (as in woodbine ‘honeysuckle’).=> band, bend, bond, bundle
- bind (v.)
- Old English bindan "to tie up with bonds" (literally and figuratively), also "to make captive; to cover with dressings and bandages" (class III strong verb; past tense band, past participle bunden), from Proto-Germanic *bindan (cognates: Old Saxon bindan, Old Norse and Old Frisian binda, Old High German binten "to bind," German binden, Gothic bindan), from PIE root *bhendh- "to bind" (see bend (v.)). Intransitive sense of "stick together" is from 1670s. Of books, from c. 1400.
- bind (n.)
- "anything that binds," in various senses, late Old English, from bind (v.). Meaning "tight or awkward situation" is from 1851.
Example
- 1. Molecules that bind to these proteins come in three flavors .
- 2. These transmitter molecules cross the gap and bind to special receptors in the downstream nerve cell .
- 3. Neurotransmitters like dopamine shuttle around and bind to specific receptors to communicate messages in the brain .
- 4. Acids tend to cause less damage than alkalis as many corneal proteins bind acid and act as a chemical buffer .
- 5. Chemical compounds that affect the functioning of genes can bind to our genetic material , turning certain genes on or off .