leave
pronunciation
How to pronounce leave in British English:
UK [liːv]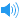
How to pronounce leave in American English:
US [liːv]

-
- Noun:
- the period of time during which you are absent from work or duty
- permission to do something
- the act of departing politely
-
- Verb:
- go away from a place
- go and leave behind, either intentionally or by neglect or forgetfulness
- act or be so as to become in a specified state
- leave unchanged or undisturbed or refrain from taking
- move out of or depart from
- make a possibility or provide opportunity for; permit to be attainable or cause to remain
- result in
- remove oneself from an association with or participation in
- put into the care or protection of someone
- leave or give by will after one's death
- have left or have as a remainder
- be survived by after one's death
- tell or deposit (information) knowledge
- leave behind unintentionally
Word Origin
- leave
- leave: [OE] English has two distinct words leave. The noun, meaning ‘permission’, comes from a prehistoric West Germanic *laubā, which was derived from a root meaning ‘pleasure, approval’ (other English words from the same source include believe and love). It passed semantically through ‘be well disposed to’ to ‘trust’ (a sense preserved in the related believe, and also in the cognate German glauben ‘believe’), and from there to ‘permit’.The verb leave ‘go away’ comes from a prehistoric Germanic *laibjan ‘remain’. It has been speculated that this is related ultimately to various Indo-European words for ‘sticky substances’ or ‘stickiness’ (Sanskrit lipta- ‘sticky’, for instance, and Greek lípos ‘grease’, source of English lipid [20]), and that its underlying meaning is ‘remaining stuck’, hence ‘staying in a place’.The sense ‘remain’ survived into English, but it died out in the 16th century, leaving as its legacy the secondary causative sense ‘cause to remain’. The apparently opposite sense ‘go away’, which emerged in the 13th century, arose from viewing the action of the verb from the point of view of the person doing the leaving rather than of the thing being left. The related German bleiben, which incorporates the prefix bi-, still retains the sense ‘remain’.Other related English words, distant and close respectively, are eclipse and eleven.=> believe, love; eclipse, eleven, lipid, twelve
- leave (v.)
- Old English læfan "to let remain; remain; have left; bequeath," from Proto-Germanic *laibijan (cognates: Old Frisian leva "to leave," Old Saxon farlebid "left over"), causative of *liban "remain," (source of Old English belifan, German bleiben, Gothic bileiban "to remain"), from root *laf- "remnant, what remains," from PIE *leip- "to stick, adhere;" also "fat." The Germanic root has only the sense "remain, continue," which also is in Greek lipares "persevering, importunate." But this usually is regarded as a development from the primary PIE sense of "adhere, be sticky" (compare Lithuanian lipti, Old Church Slavonic lipet "to adhere," Greek lipos "grease," Sanskrit rip-/lip- "to smear, adhere to." Seemingly contradictory meaning of "depart" (early 13c.) comes from notion of "to leave behind" (as in to leave the earth "to die;" to leave the field "retreat").
- leave (n.)
- "permission," Old English leafe "leave, permission, license," dative and accusative of leaf "permission," from Proto-Germanic *lauba (cognates: Old Norse leyfi "permission," Old Saxon orlof, Old Frisian orlof, German Urlaub "leave of absence"), from PIE *leubh- "to care, desire, love, approve" (see love (n.)). Cognate with Old English lief "dear," the original idea being "approval resulting from pleasure." Compare love, believe. In military sense, it is attested from 1771.
Example
- 1. Did you leave the building ?
- 2. Jack lets the man leave .
- 3. How can you leave alone ?
- 4. They rarely leave the building .
- 5. But you can never leave !