shake
pronunciation
How to pronounce shake in British English:
UK [ʃeɪk]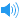
How to pronounce shake in American English:
US [ʃeɪk]

-
- Noun:
- building material used as siding or roofing
- frothy drink of milk and flavoring and sometimes fruit or ice cream
- a note that alternates rapidly with another note a semitone above it
- grasping and shaking a person's hand (as to acknowledge an introduction or to agree on a contract)
- reflex shaking caused by cold or fear or excitement
- causing to move repeatedly from side to side
-
- Verb:
- move or cause to move back and forth
- move with or as if with a tremor
- shake or vibrate rapidly and intensively
- move back and forth or sideways
- undermine or cause to waver
- stir the feelings, emotions, or peace of
- get rid of
- bring to a specified condition by or as if by shaking
- shake (a body part) to communicate a greeting, feeling, or cognitive state
Word Origin
- shake
- shake: [OE] Shake is a general Germanic verb, although today its only surviving relatives are Swedish skaka and Norwegian skage. It comes from a prehistoric Germanic *skakan, which goes back to the Indo-European base *skeg-, *skek- (source also of Sanskrit khajati ‘agitate, churn’ and Welsh ysgogi ‘move’).
- shake (v.)
- Old English sceacan "move (something) quickly to and fro, brandish; move the body or a part of it rapidly back and forth;" also "go, glide, hasten, flee, depart" (related to sceacdom "flight"); of persons or parts of the body, "to tremble" especially from fever, cold, fear" (class VI strong verb; past tense scoc, past participle scacen), from Proto-Germanic *skakanan (cognates: Old Norse, Swedish skaka, Danish skage "to shift, turn, veer"). No certain cognates outside Germanic, but some suggest a possible connection to Sanskrit khaj "to agitate, churn, stir about," Old Church Slavonic skoku "a leap, bound," Welsh ysgogi "move." Of the earth in earthquakes, c. 1300. Meaning "seize and shake (someone or something else)" is from early 14c. In reference to mixing ingredients, etc., by shaking a container from late 14c. Meaning "to rid oneself of by abrupt twists" is from c. 1200, also in Middle English in reference to evading responsibility, etc. Meaning "weaken, impair" is from late 14c., on notion of "make unstable." To shake hands dates from 1530s. Shake a (loose) leg "hurry up" first recorded 1904; shake a heel (sometimes foot) was an old way to say "to dance" (1660s); to shake (one's) elbow (1620s) meant "to gamble at dice." Phrase more _____ than you can shake a stick at is attested from 1818, American English. To shake (one's) head as a sign of disapproval is recorded from c. 1300.
- shake (n.)
- late 14c., "charge, onrush," from shake (v.). Meaning "a hard shock" is from 1560s. From 1580s as "act of shaking;" 1660s as "irregular vibration." The hand-grip salutation so called by 1712. As a figure of instantaneous action, it is recorded from 1816. Phrase fair shake "honest deal" is attested from 1830, American English (Bartlett calls it "A New England vulgarism"). The shakes "nervous agitation" is from 1620s. Short for milk shake from 1911. Dismissive phrase no great shakes (1816, Byron) perhaps is from dicing.
Example
- 1. There are multiple risks that can shake confidence .
- 2. Regulators may take action but will be careful not to shake confidence further .
- 3. Yet it is hard to shake the scepticism entirely .
- 4. Eg. the visitors shake hand sit down at the table .
- 5. In that case , disabling aero snap and aero shake is the best option .