meridian
发音
英 [məˈrɪdiən]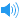
美 [məˈrɪdiən]

-
- [医]经(中医学)
- [地名] [美国] 默里迪恩
单词词源
meridian 子午线,经线
来自拉丁语meridies,中午,来自medius,中间的,词源同middle,字母d被r音化,dies,天,词源同diurnal.引申词义中午的太阳,并用于地理学术语子午线,经线。
双语例句
- 1. Of or relating to meridians or a meridian .
- 子午线的子午线的或与子午线有关的。
- 2. The meridian was a very understandable derivative from what was probably the most ancient astronomical instrument of all , the gnomon , used for measuring the different lengths of the sun 's shadow .
- 我们很容易理解子午线是从圭表衍生出来的,圭表是中国古代用来度量日影长度的天文仪器,很可能是所有天文仪器中最古老的。
- 3. Looking south , the observer measured the shadow at noon ; looking north during the night , he measured the times at which the various circumpolar made their upper and lower transits across the meridian .
- 向南看,观测者可以测量中午的日影;夜间向北看,观测者可以测出不同拱极星通过上半子午线和下半子午线的次数。
- 4. Their astronomical system was thus closely associated with the concept of the meridian ( the great circle of the celestial sphere passing through the pole star and the observer 's zenith ) , and they determined systematically the culminations and lower transits ( meridian passages ) of these circumpolar stars .
- 因此,他们的天文学体系与子午线(天球绕过北极星和观测者的天顶产生的大圆弧)的概念有密切联系,系统化地决定了拱极星的中天和下中天(中天)。
- 5. Meridian circulation is closely related to life . Life would end , if meridian circulation stops .
- 经络循行是与生命共存的:经络循行停止,生命则终结。