get
pronunciation
How to pronounce get in British English:
UK [ɡet]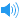
How to pronounce get in American English:
US [ɡet]

-
- Verb:
- come into the possession of something concrete or abstract
- enter or assume a certain state or condition
- cause to move; cause to be in a certain position or condition
- receive a specified treatment (abstract)
- reach a destination; arrive by movement or progress
- go or come after and bring or take back
- of mental or physical states or experiences
- take vengeance on or get even
- achieve a point or goal
- cause to do; cause to act in a specified manner
- succeed in catching or seizing, especially after a chase
- come to have or undergo a change of (physical features and attributes)
- be stricken by an illness, fall victim to an illness
- communicate with a place or person; establish communication with, as if by telephone
- give certain properties to something
- move into a desired direction of discourse
- grasp with the mind or develop an undersatnding of
- attract and fix
- reach with a blow or hit in a particular spot
- reach by calculation
- acquire as a result of some effort or action
- purchase
- perceive by hearing
- suffer from the receipt of
- receive as a retribution or punishment
- leave immediately; used usually in the imperative form
- reach and board
- irritate
- evoke an emotional response
- apprehend and reproduce accurately
- in baseball: earn or achieve a base by being walked by the pitcher
- overcome or destroy
- be a mystery or bewildering to
- take the first step or steps in carrying out an action
- undergo (as of injuries and illnesses)
- make children
Word Origin
- get
- get: [13] Get, now one of the most pervasive of English words, has only been in the language for the (comparatively) short period of 800 years. It was borrowed from Old Norse geta (although a related, hundred-per-cent English -get, which occurs in beget and forget, dates back to Old English times). Both come via a prehistoric Germanic *getan from Indo-European *ghed-, which signified ‘seize’ (guess is ultimately from the same source). Gotten is often quoted as an American survival of a primeval past participle since abandoned by British English, but in fact the original past participle of got was getten, which lasted into the 16th century; gotten was a Middle English innovation, based on such models as spoken and stolen. Got originated as an abbreviated form of gotten, which in due course came to be used, on both sides of the Atlantic, as the past tense of the verb (replacing the original gat).=> beget, forget, guess
- get (v.)
- c. 1200, from Old Norse geta (past tense gatum, past participle getenn) "to obtain, reach; to be able to; to beget; to learn; to be pleased with," a word of very broad meaning, often used almost as an auxilliary verb, also frequently in phrases (such as geta rett "to guess right"). This is from Proto-Germanic *getan (cognates: Old Swedish gissa "to guess," literally "to try to get"), from PIE root *ghend-, also *ghed- "seize, take" (cognates: Greek khandanein "to hold, contain," Lithuanian godetis "be eager," second element in Latin prehendere "to grasp, seize," Welsh gannu "to hold, contain," Old Church Slavonic gadati "to guess, suppose"). Old English, as well as Dutch and Frisian, had the verb almost exclusively in compounds (such as begietan, "to beget;" forgietan "to forget"). Vestiges of an Old English cognate *gietan remain obliquely in modern past participle gotten and original past tense gat, also Biblical begat. In compound phrases with have and had it is grammatically redundant, but often usefully indicates possession, obligation, or necessity, or gives emphasis. The word and phrases built on it take up 29 columns in the OED 2nd edition; Century Dictionary lists seven distinct senses for to get up. "I GOT on Horseback within ten Minutes after I received your Letter. When I GOT to Canterbury I GOT a Chaise for Town. But I GOT wet through before I GOT to Canterbury, and I HAVE GOT such a Cold as I shall not be able to GET rid of in a Hurry. I GOT to the Treasury about Noon, but first of all I GOT shaved and drest. I soon GOT into the Secret of GETTING a Memorial before the Board, but I could not GET an Answer then, however I GOT Intelligence from the Messenger that I should most likely GET one the next Morning. As soon as I GOT back to my Inn, I GOT my Supper, and GOT to Bed, it was not long before I GOT to Sleep. When I GOT up in the Morning, I GOT my Breakfast, and then GOT myself drest, that I might GET out in Time to GET an Answer to my Memorial. As soon as I GOT it, I GOT into the Chaise, and GOT to Canterbury by three: and about Tea Time, I GOT Home. I HAVE GOT No thing particular for you, and so Adieu." [Philip Withers, "Aristarchus, or the Principles of Composition," London, 1789, illustrating the widespread use of the verb in Modern English] As a command to "go, be off" by 1864, American English. Meaning "to seize mentally, grasp" is from 1892. Get wind of "become acquainted with" is from 1840, from earlier to get wind "to get out, become known" (1722). To get drunk is from 1660s; to get religion is from 1772; to get better "recover health" is from 1776. To get ready "prepare oneself" is from 1890; to get going "begin, start doing something" is by 1869 in American English; get busy "go into action, begin operation" is from 1904. Get lost as a command to go away is by 1947. To get ahead "make progress" is from 1807. To get to (someone) "vex, fret, obsess" is by 1961, American English (get alone as "to puzzle, trouble, annoy" is by 1867, American English). To get out of hand originally (1765) meant "to advance beyond the need for guidance;" sense of "to break free, run wild" is from 1892, from horsemanship. To get on (someone's) nerves is attested by 1970.
- get (n.)
- early 14c., "offspring, child," from get (v.) or beget. Meaning "what is got, booty" is from late 14c.
Antonym
Example
- 1. What exactly do you get ?
- 2. So what did we get ?
- 3. What job can I get ?
- 4. But how did you get it ?
- 5. Borrowers could no longer get credit .